Skeleton Key Group Case 18 Filling in the Gap Renal Fellow Network
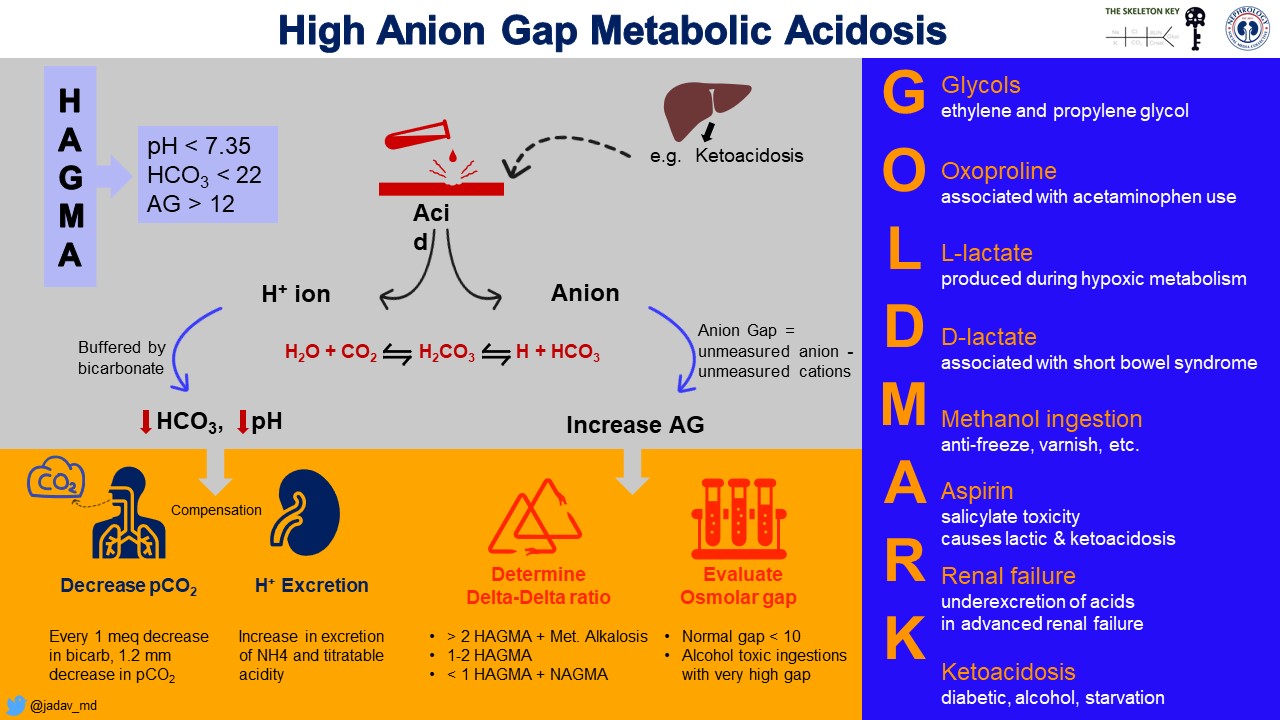
A mnemonic to remember the commonest causes of anion gap metabolic acidosis is: GOLDMARK Mnemonic G: glycols (ethylene glycol and propylene glycol) O: oxoproline L: L-lactate D: D-lactate M: methanol A: aspirin R: renal failure K: ketoa.

clinical clerkship mnemonics
High anion gap metabolic acidosis (HAGMA) is a subcategory of acidosis of metabolic (i.e., non-respiratory) etiology. Differentiation of acidosis into a particular subtype, whether high anion gap metabolic acidosis or non-anion gap metabolic acidosis (NAGMA), aids in the determination of the etiology and hence appropriate treatment.[1][2][3][4]

Dx Schema Anion gap metabolic acidosis The Clinical Problem Solvers
A helpful mnemonic called "GOLDMARK" can be used when evaluating causes of elevated anion gap metabolic acidoses such as in this case [5]. These include glycols (ethylene and propylene.
ABG Interpretation The Anion Gap (Lesson 5) YouTube
A Lancet Editorial1 in 1977, referring to an article entitled "Clinical use of the anion gap"2 opined: "In an age when all too often plasma-electrolyte measurements are ordered without any deliberate judgment being made as to the likely usefulness of the result, it is refreshing to have a reminder of the subtleties involved in the interpretation of this commonest set of clinical.
PPT Anion Gap PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2865703
High-Anion-Gap Metabolic Acidosis During a Prolonged Hospitalization Following Perforated Diverticulitis: An Educational Case Report. Cecilia Farfan Ruiz A , Sriperumbuduri S , Shaw JLV , Clark EG. Can J Kidney Health Dis, 9:20543581221129753, 28 Oct 2022. Cited by: 0 articles | PMID: 36325264 | PMCID: PMC9619282. Free to read & use.

Anion gap calculation, anion gap blood test & causes of high or low anion gap
GOLDMARK mnemonic for anion gap metabolic acidosis Glycols (ethylene glycol & propylene glycol) Oxoproline (metabolite of acetaminophen) L-lactate D-lactate (acetaminophen, short bowel syndrome, propylene glycol infusions for lorazepam and phenobarbital) Methanol ASA Renal Failure

Medical Mnemonics
The most common causes of high anion gap metabolic acidosis (HAGMA) are listed in Table 1. They are arranged as the mnemonic "GOLDMARK" (Glycols [ethylene, pro-pylene, and diethylene], 5-Oxoproline [acetaminophen], L-Lactic Acid, D-Lactic acid, Methanol, Aspirin, Renal fail-ure, Ketoacidosis). In contrast, when metabolic acidosis is due to.
anion gap 判讀 Hanxngde
GOLD MARK is a new mnemonic recommended to replace MUDPILES for causes of anion-gap metabolic acidosis. GOLD MARK. G lycols (propylene glycol and ethylene glycol); O xoproline - 5-oxoproline (or pyroglutamic acid) is associated with chronic acetaminophen use, often by malnourished women.; L-lactate,; D-lactate - D-lactic acid can occur in some patients with short bowel syndromes

The Anion Gap in Metabolic Acidosis YouTube
A useful mnemonic for the differential diagnosis of increased anion gap metabolic acidosis is GOLDMARK (glycols [ethylene glycol and propylene glycol], oxoproline, L-lactate, D-lactate, methanol, aspirin, renal failure, and ketoacidosis) (Table 21-13). + + Table 21-13. Common causes and therapy for increased anion gap metabolic acidosis..

High Anion Gap Tool Medical mnemonics, Medical laboratory science, Nursing mnemonics
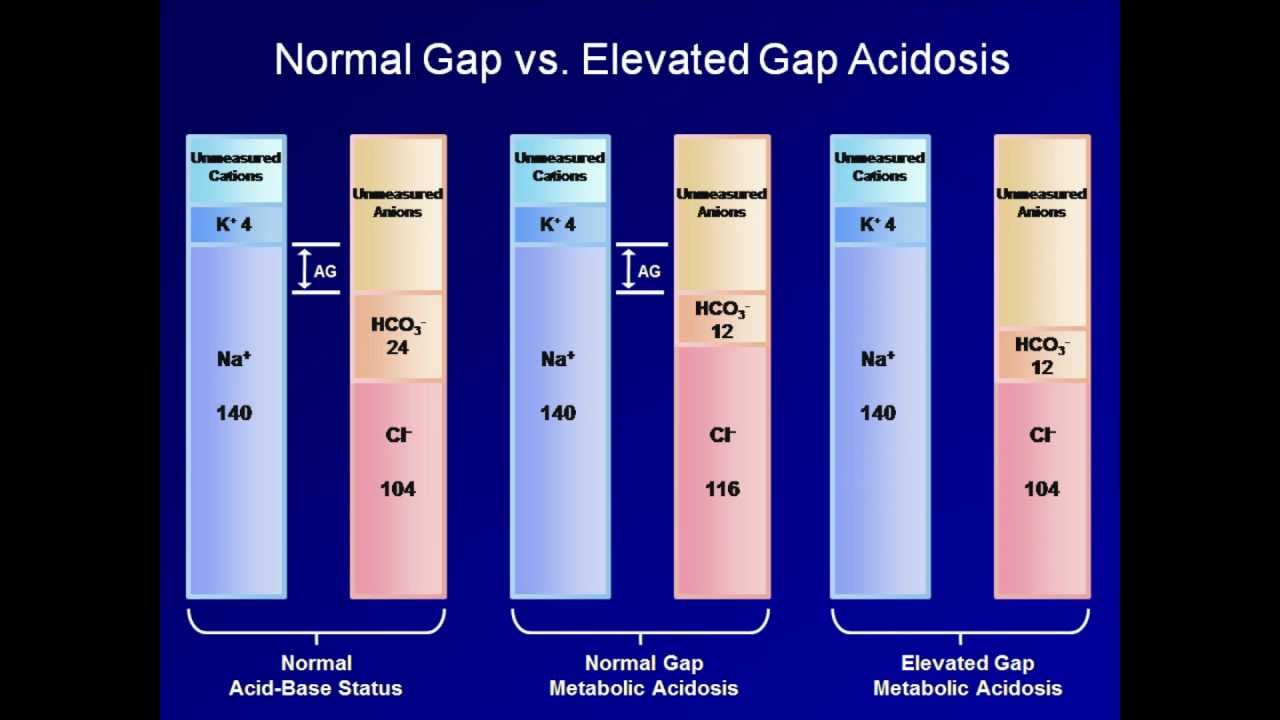
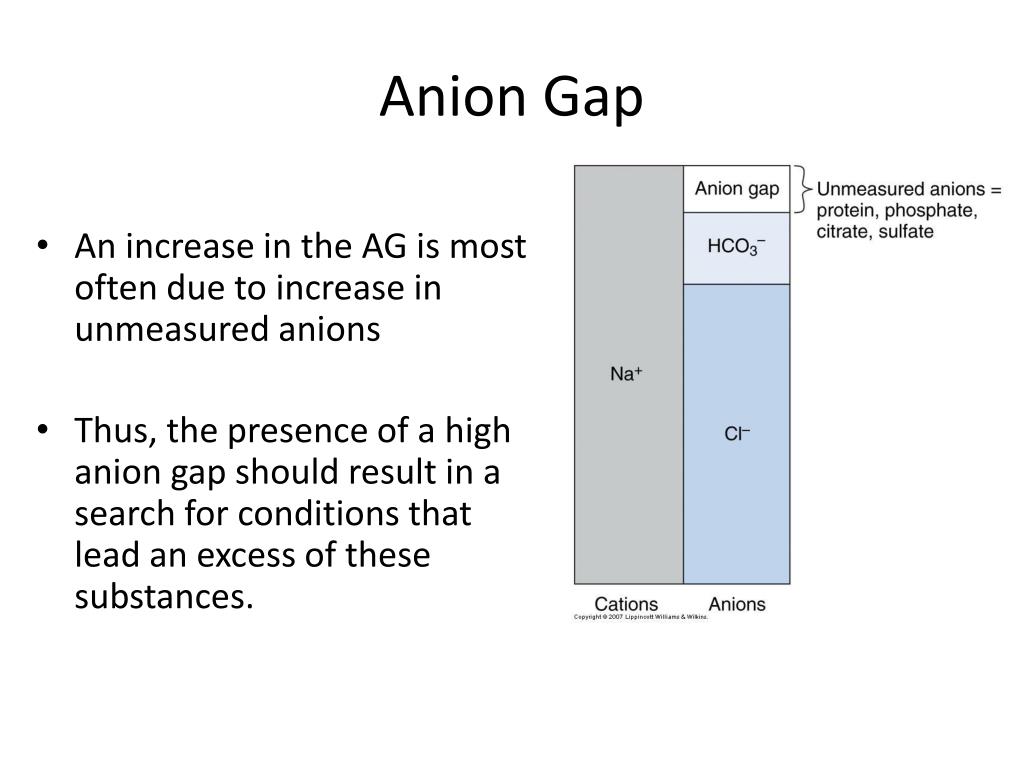
High anion gap metabolic acidosis is a form of metabolic acidosis characterized by a high anion gap (a medical value based on the concentrations of ions in a patient's serum). Metabolic acidosis occurs when the body produces too much acid, or when the kidneys are not removing enough acid from the body. Several types of metabolic acidosis occur, grouped by their influence on the anion gap.

Anion gap calculation, anion gap blood test & causes of high or low anion gap
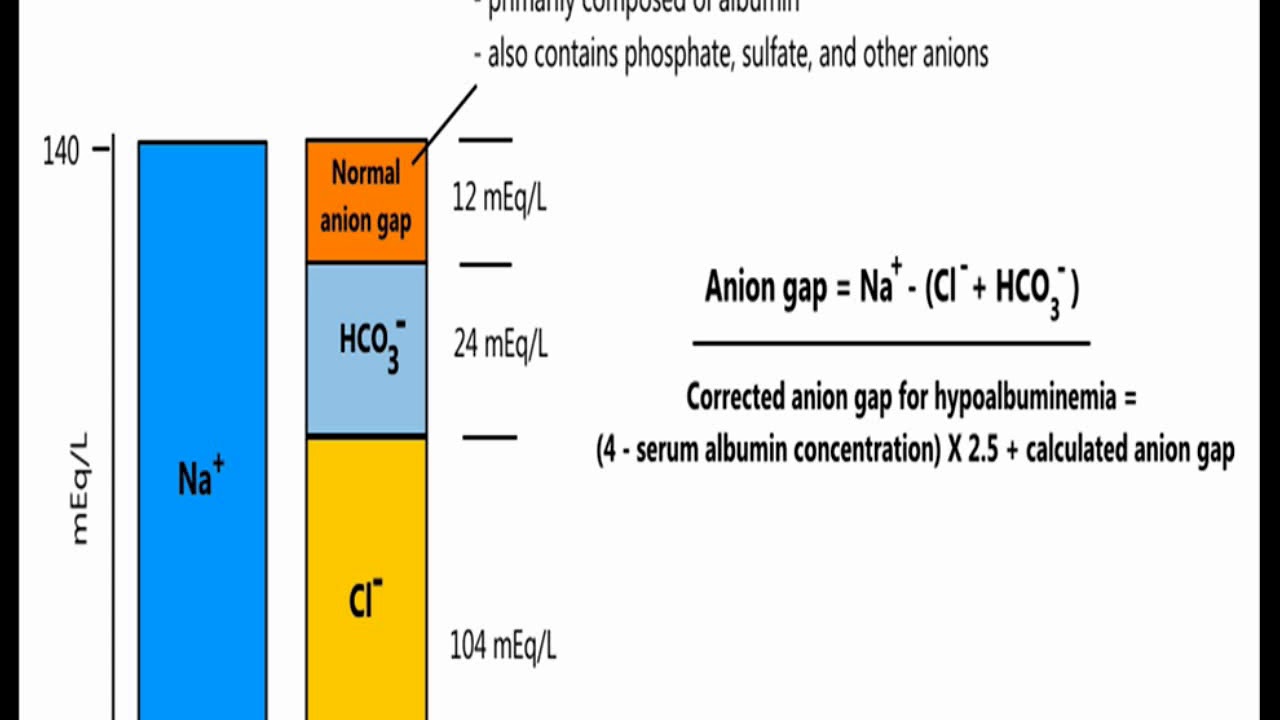
The anion gap is a measurement of the difference — or gap — between the negatively charged and positively charged electrolytes. Each of the above electrolytes is individually measured in a comprehensive metabolic blood test panel and electrolyte blood test panel. Laboratory scientists then calculate the anion gap based on those measurements.

The anion gap; its merits and demerits Deranged Physiology
The GOLDMARK mnemonic is helpful in recalling causes of a HAGMA (Table 2).[[5]] Table 2: GOLDMARK mnemonic showing causes for a high anion gap metabolic acidosis.. Diagnosis requires clinical suspicion based on raised anion gap, exclusion of more common causes and the presence of relevant risk factors.[[3]] Formal diagnosis of pyroglutamic.
Anion Gap Meaning, Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and More
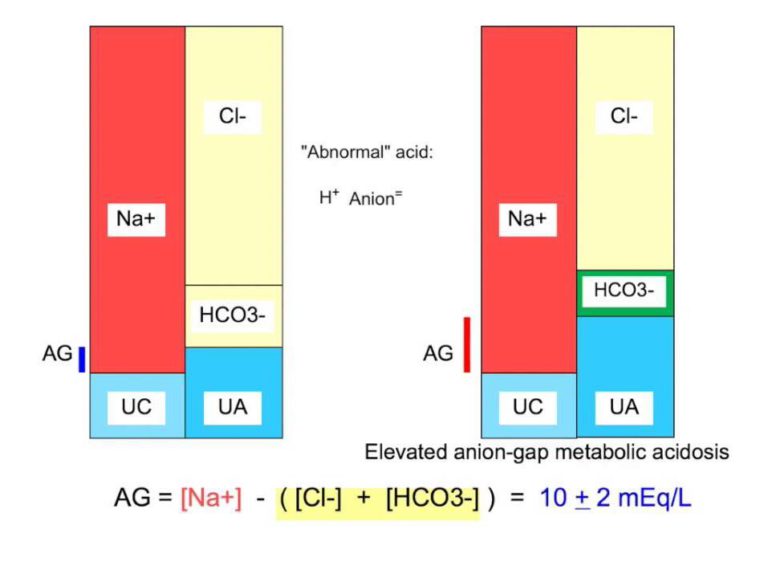
the basis of an anion gap calculation (Na+[Cl-HCO 3 -]): the high-anion-gap metabolic acidoses, and the normal-anion-gap, or hyperchloraemic, metabolic acidoses. Two popular mnemonics are often used to remember the major causes of the high-gap metabolic acidoses. The fi rst is KUSMALE (a useful misspelling of Adolph Kussmaul's name), which

Normal Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Mnemonic
The GOLDMARK mnemonic for anion gap metabolic acidosis is more useful. GOLDMARK mnemonic for anion gap metabolic acidosis; Glycols (ethylene glycol & propylene glycol) Oxoproline (metabolite of acetaminophen) L-lactate. D-lactate (acetaminophen, short bowel syndrome, propylene glycol infusions for lorazepam and phenobarbital)

An Unexpected Gap Effects of Salicylates and Other Conditions on the Serum Anion Gap AJKD Blog
Mnemonic for causes: the mnemonic GOLDMARK replaces the older MUDPILERS and is a more accurate reflection of common modern causes of anion gap acidosis. The starred conditions are the most common causes.. Serum anion gap: its uses and limitations in clinical medicine. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2007;2(1):162-74. Kraut JA, Mullins ME. Toxic.

Medical Mnemonics Causes of Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis “GOLD MARK” USMLE / Internal
GOLD MARK: an anion gap mnemonic for the 21st century. GOLD MARK: an anion gap mnemonic for the 21st century. GOLD MARK: an anion gap mnemonic for the 21st century Lancet. 2008 Sep 13;372(9642):892. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61398-7. Authors Ankit N Mehta, Joshua B Emmett, Michael Emmett. PMID:.